Concerns as ’most contagious’ Covid variant spreads in Europe
Health authorities have expressed concern over a new Covid strain’s rapid spread in Europe as the US approves use of the Novavax vaccine.
World
Don't miss out on the headlines from World. Followed categories will be added to My News.
The Netherlands has become the latest country to detect a case of the Covid Omicron subvariant BA. 2.75, as experts expressed concern about the strain’s rapid spread.
The subvariant, nicknamed “Centaurus”, first emerged in India in May and has since spread to around 10 countries, including the United States, Britain, Germany and Australia.
It “has also now been identified in the Netherlands,” the Dutch National Institute of Public Health said in a statement.
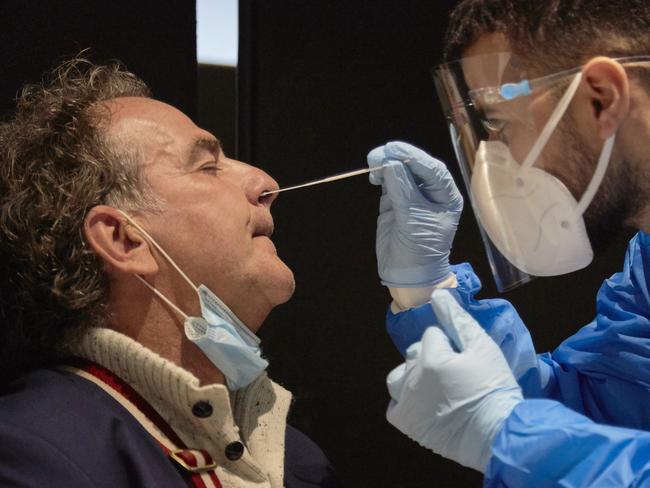
“Little is known about BA. 2.75,” the institute said, but it “appears to more easily bypass the defences built up against SARS-CoV-2 through small, specific changes”.
The World Health Organisation’s chief scientist Soumya Swaminathan said last week that the UN agency was closely tracking the strain, but there were “limited sequences to analyse”.
“This sub-variant seems to have a few mutations on the receptor binding domain of the spike protein … so we have to watch that,” she said in a tweeted video.
She added that it was “too early to know” how well the strain can evade immunity or how severe it was.

Antoine Flahault, director of the Institute of Global Health at the University of Geneva, told AFP that BA. 2.75’s spread in India indicated it could be more transmissible than the BA. 5 Omicron subvariant, which has been driving waves in Europe and the US.
“It seems to be becoming the dominant strain in India — the question is will it become the dominant strain all over the world?” Flahault added that previous dominant strains, like Delta, had first taken over the country they emerged in before spreading across the world.
But he said there was a “margin of unpredictability,” pointing to how BA. 2.12.1 became dominant in the US but BA. 5 “succeeded” when the two came in direct competition.

Flahault added that successive variants made developing a vaccine to fight them more difficult, because by the time one jab targeting them was ready to be rolled out, newer strains had taken over.
It was far too early to know about the severity of BA. 2.75, he added. The Dutch sample was collected in the northern region of Gelderland on June 26, the institute said, adding it was “closely monitoring the situation” there.
Earlier this month, the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control listed BA. 2.75 as a “variant under monitoring”.
US SIGNS OFF ON NOVAVAX VACCINE
The US Food and Drug Administration on Wednesday authorised Novavax’s Covid-19 shot for use in people aged 18 and over, expanding Americans’ options for vaccination against the disease.
The vaccine — which is produced by an American company — is already available in dozens of other countries. Just three Covid shots, two of them based on messenger RNA technology, have been previously authorised in the United States.
The emergency authorisation of the Novavax vaccine “offers adults in the United States who have not yet received a Covid-19 vaccine another option that meets the FDA’s rigorous standards for safety, effectiveness and manufacturing quality,” the FDA’s commissioner Robert Califf said in a statement.
Administered in two doses three weeks apart, the Novavax vaccine uses a more conventional technology than the mRNA shots, which have been the subject of numerous conspiracy theories, though they have been proven to be safe.
Novavax’s vaccine contains part of the virus that triggers an immune response — the approach used by many other common shots.
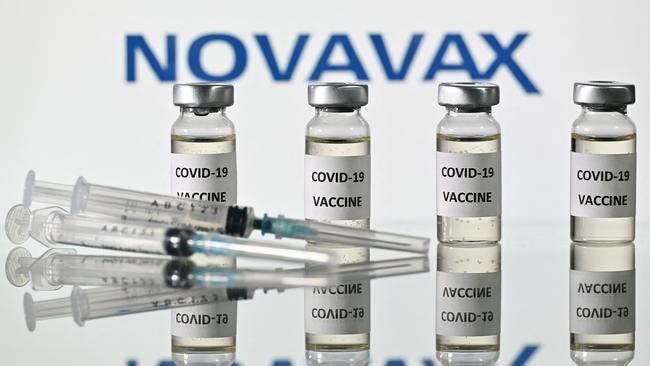
In clinical trials involving thousands of people in the United States and Mexico, it was 90 per cent effective against symptomatic cases of Covid-19. However, the trials were conducted prior to the emergence of the Delta and Omicron variants of the disease.
The vaccination rate of adults in the United States has stagnated at around 77 per cent.
The US government had announced this week that it had purchased 3.2 million Novavax doses in anticipation of the FDA decision.
FAUCI’S STUNNING ADMISSION
White House chief medical adviser Dr Anthony Fauci has admitted that Covid-19 vaccines do not protect “overly well” against infection.
It is a stark turnaround from early hopes that the experimental treatments would bring an end to the global coronavirus pandemic.
Speaking to Fox News, Fauci said the ineffectiveness of the vaccines at preventing infection were reason to get more boosters of the vaccine.
“One of the things that’s clear from the data [is] that even though vaccines – because of the high degree of transmissibility of this virus – don’t protect overly well, as it were, against infection, they protect quite well against severe disease leading to hospitalisation and death,” he said.
“And I believe that’s the reason … why at my age, being vaccinated and boosted, even though it didn’t protect me against infection, I feel confident that it made a major role in protecting me from progressing to severe disease.”
He added on CNN that any immunity against infection wanes relatively quickly and “goes way, way down”, with the new BA. 5 variant increasing the likelihood of reinfection for people that have already been infected.

Recognising that advocating for more of a vaccine that he admitted doesn’t prevent infection, Fauci said it was “very likely” he had a mild case of Covid due to being vaccinated.
“So my message to people who seem confused because people who are vaccinated get infected – the answer is if you weren’t vaccinated, the likelihood [is] you would have had [a] more severe course than you did have when you were vaccinated,” he told Fox News.
It comes as the World Health Organisation said the fresh surge of Covid infections showed the virus was running free and the pandemic is nowhere near over.
Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said he was worried that case numbers were shooting up, putting more strain on health systems and workers.
The number of Covid cases reported to the WHO increased 30 per cent in the past two weeks, driven by sub-variants of the Omicron strain and the lifting of control measures.
“New waves of the virus demonstrate again that Covid-19 is nowhere near over. As the virus pushes at us, we must push back,” he insisted.
He told a news conference that as transmission increases, governments must also deploy tried-and-tested measures like mask-wearing and improving ventilation.

“Sub-variants of Omicron, like BA. 4 and BA. 5, continue to drive waves of cases, hospitalisation and death around the world,” Tedros said.
“Surveillance has reduced significantly – including testing and sequencing – making it increasingly difficult to assess the impact of variants on transmission, disease characteristics, and the effectiveness of countermeasures.”
Furthermore, tests, treatments and vaccines are not being deployed effectively.
“The virus is running freely and countries are not effectively managing the disease burden based on their capacity,” he said, both in terms of hospitalisation of acute cases and the expanding number of people with Long Covid.
‘UNCERTAIN AND UNPREDICTABLE’
The WHO’s Covid-19 emergency committee met Friday via videoconference and determined the pandemic remains a Public Health Emergency of International Concern – the highest alarm the WHO can sound.
WHO emergencies director Michael Ryan told the meeting recent changes in testing policies were hindering the detection of cases and the monitoring of virus evolution.
The committee stressed the need to reduce transmission as the implications of a pandemic caused by a new respiratory virus would not be fully understood, the WHO said in a statement on Monday.

The group voiced concern over steep reductions in testing, resulting in reduced surveillance and genomic sequencing.
“This impedes assessments of currently circulating and emerging variants of the virus,” the WHO said, feeding the inability to interpret trends in transmission.
The committee said the trajectory of virus evolution and the characteristics of emerging variants remained “uncertain and unpredictable”.
It said the absence of measures to reduce transmission increasing the likelihood of “new, fitter variants emerging, with different degrees of virulence, transmissibility, and immune escape potential”.
BOOSTER BOOST
Meanwhile the WHO’s European office recommended second booster doses of a Covid vaccine for older people and vulnerable groups.
Covid cases have been rising sharply since the end of May around most of Europe. The call followed the EU’s health and medicine agencies recommendation on Monday of a second booster shot for people over 60 years old.
Coronavirus cases have risen 57 per cent in Moscow over the past week, the Russian capital’s health authorities said.
“We recommend that you wear a mask in public places because the new Omicron sub-variants BA. 4 and BA. 5 spread more rapidly from person to person,” Moscow social services wrote on Telegram.

And hundreds of thousands of people were under lockdown in a small Chinese city after just one case of Covid-19 was detected, as Beijing’s strict no-tolerance virus strategy showed no sign of abating.
The steelmaking hub of Wugang in Henan province announced three days of “closed control”.
None of the city’s 320,000 people are allowed outside their homes until midday Thursday. Local authorities were to deliver basic necessities.
China is the last major economy glued to a zero-Covid policy, crushing new outbreaks with snap lockdowns, forced quarantines and onerous travel curbs despite mounting public fatigue and damage to the economy.
More Coverage
Originally published as Concerns as ’most contagious’ Covid variant spreads in Europe




