The biggest challenges facing Australia’s booming regions revealed
Pandemic migration has exposed the ‘gaps’ in regional community infrastructure right across Australia, from water security, telecommunications to affordable housing. See the biggest issues in your region.
Property
Don't miss out on the headlines from Property. Followed categories will be added to My News.
The great pandemic migration has exposed the ‘gaps’ in regional community infrastructure right across Australia, from water security and telecommunications to education and affordable housing.
A landmark report by Infrastructure Australia reveals where those gaps and vulnerabilities are, and many are in locations that have benefited, or in some cases been overwhelmed, by the exodus to affordable lifestyle, a trend that was supercharged during the Covid-19 pandemic.
The report identified 479 infrastructure gaps across 48 of Australia’s regions through vast consultation with government, community representatives and industry stakeholders.
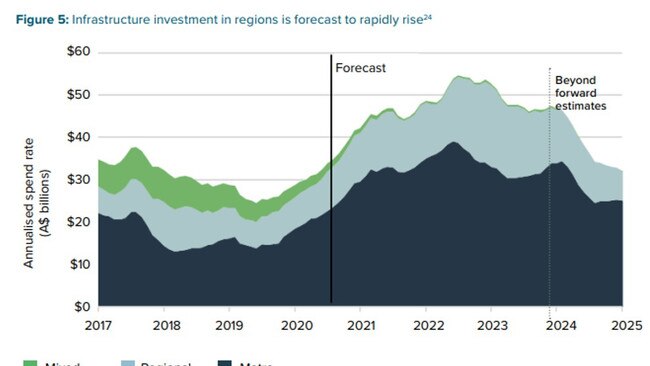
Housing and telecommunications were the two biggest issues identified across around half of the regional locations.
MORE: Meet the new owner of Australia’s hottest house
Surprise location where Australian sellers are happiest
Red flags loom large for interstate property buyers

“It feels like we’re always playing catch-up,” a workshop participant in Queensland said.
“Instead of anticipating future needs and planning accordingly, we’re just fixing problems and getting by.
“We need to be more proactive and we need support from all levels of government to be able to do that.”
While the participants saw the pandemic population shift as having the potential to be a “real catalyst for change” in the regions, many reported problems with attracting skilled workers due to issues such as “housing supply and access to basic services like childcare and healthcare”.
Existing strengths across the regions included natural environments (45 of 48 regions), gateway ports (33), education and research institutions (32), natural resources (26), health (14, water (1) and community infrastructure (5).

Gaps in availability, diversity and affordability of housing was the biggest issue facing 26 of the 48 regions, followed by broadband and mobile connectivity (23), water security (22), access to further education and skills training (19) and public transport (15).
Road (12) and freight (9) infrastructure, energy (7), health and aged care access (3) and recreation infrastructure (3) were also issues facing growing regional communities, according to the national report.

“Local stakeholders across Regional Australia highlighted a lack of appropriate housing as being a major constraint in attracting and retaining skilled workers to the regions, many of
which are already experiencing skills shortages,” the report said.
“In this sense, poor housing availability, diversity and affordability in the regions is inhibiting
capacity for population and economic growth.”
The Regional Strengths and Infrastructure Gaps report provides government, industry, businesses and the community with a guide to support record migration and further growth, off the back of the 200 per cent increase in growth in Australia’s regional areas in 2019/2020. This regionalisation trend has continued with the first quarter of 2021 being the largest internal migration on record, according to the report.

Australian home values rose 25 per cent, a record high, between March 2002 and February 2022, according to CoreLogic.
Vacancy rates across many regions have also plummeted to record lows, with the lack of available housing leading to skills shortages in many areas.
Infrastructure Australia CEO Romilly Madew said the significant upswing in regionalisation, which was further accelerated by the pandemic, had compounded pressure on already stretched regional infrastructure assets and networks.
“By drawing out commonalities where they exist, we are aiming to improve information sharing and enable a coordinated, forward-looking view of the challenges and opportunities in Regional Australia,” she said.

THE GAPS
QUEENSLAND
Central and Western Qld: Water security; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure; Broadband and mobile connectivity
Darling Downs and South West: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Water security
Gold Coast: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure; Broadband and mobile connectivity

Ipswich and West Moreton: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Access to further education and skills training; Water security
Logan and Redlands: Access to further education and skills training; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Provision, quality and protection of green, blue and recreation infrastructure
Moreton Bay: Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Industry-enabling infrastructure to support growth and innovation
Greater Whitsundays: Distribution, transmission and generation of energy; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Industry-enabling infrastructure to support growth and innovation
Sunshine Coast: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Access to further education and skills training; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing
Townsville and North West: Distribution, transmission and generation of energy; Access to further education and skills training; Water security

Tropical North: Water security; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure; Distribution, transmission and generation of energy
Wide Bay Burnett: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Water security; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing
NEW SOUTH WALES
Central Coast: Access to further education and skills training; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing
Central West: Connectivity, capacity and quality of freight infrastructure; Water security; Access to further education and skills training
Far South Coast: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure
Far West: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Access to further education and skills training; Water security
Hunter: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Access to further education and skills training; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing

Illawarra: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Mid North Coast: Access to further education and skills training; Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure
Murray: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Access to further education and skills training; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing
Northern Inland: Water security; Access to further education and skills training; Broadband and mobile connectivity
Northern Rivers: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Water security; Industry-enabling infrastructure to support growth and Industry-enabling infrastructure to support growth and innovation
Orana: Access to further education and skills training; Provision, quality and protection of green, blue and recreation; infrastructure; Water security
Riverina: Access to further education and skills training; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing; Water security
Southern Inland: Availability, affordability and diversity of housing; Waste management and resource recovery; Water security
VICTORIA
Barwon South West: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Industry-enabling infrastructure to support growth and innovation
Gippsland: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure; Natural disaster resilience

Grampians: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Distribution, transmission and generation of energy
Hume: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport
Loddon Mallee: Access to further education and skills training; Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport
SOUTH AUSTRALIA
Adelaide Hills, Fleurieu and Kangaroo Island: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Adelaide Metropolitan: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure; Water security

Barossa Gawler Light Adelaide Plains: Water security; Access to and capacity of health and aged care infrastructure; Broadband and mobile connectivity
Far North: Water security; Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Limestone Coast: Access to further education and skills training; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Murraylands and Riverland: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Eyre Peninsula: Water security; Access to and capacity of health and aged care infrastructure; Distribution, transmission and generation of energy
Yorke and Mid North: Water security; Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing
WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Goldfields-Esperance: Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Access to further education and skills training; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure
Great Southern: Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure; Water security; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing
Kimberley: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure
Mid West Gascoyne: Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure; Broadband and mobile connectivity
Peel: Water security; Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Access to further education and skills training; Capacity, connectivity and quality of freight infrastructure
Pilbara: Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Access to further education and skills training; Distribution, transmission and generation of energy

South West: Access to further education and skills training; Water security; Industry enabling infrastructure to support growth and innovation
Wheatbelt: Broadband and digital connectivity; Water security; Distribution, transmission and generation of energy
TASMANIA
Tasmania: Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Access to and capacity of health and aged care infrastructure; Capacity, quality and accessibility of early, primary and; secondary education

NORTHERN TERRITORY
Northern Territory: Broadband and mobile connectivity; Capacity, connectivity and quality of road infrastructure; Availability, affordability and diversity of housing
AUSTRALIAN CAPITAL TERRITORY
ACT: Capacity, connectivity and quality of public transport; Availability, diversity and affordability of housing; Provision, quality and protection of green, blue and recreation infrastructure
Originally published as The biggest challenges facing Australia’s booming regions revealed



