University of Tasmania researchers say thylacine may still exist in southwest wilderness
Groundbreaking new research suggests the thylacine may have survived into the 2000s — and there’s a chance they may still exist in Tasmania’s southwest. LATEST >>
Tasmania
Don't miss out on the headlines from Tasmania. Followed categories will be added to My News.
A team of international researchers has claimed there is “a very small chance” the thylacine still exists in the remote Tassie wilderness.
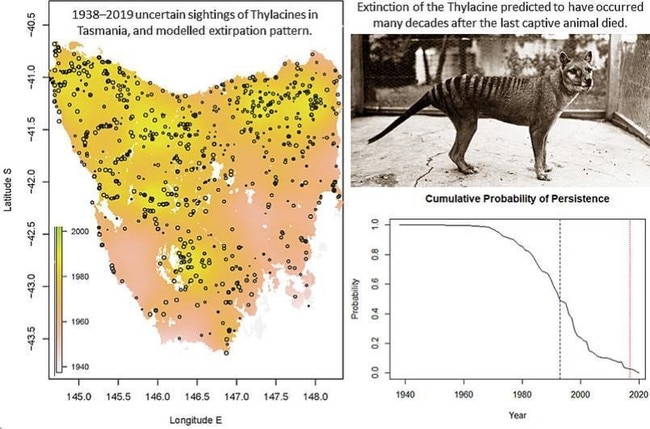
A new study, led by University of Tasmania professor of environmental sustainability Barry Brook, used a comprehensive database of 1237 observational records from Tasmania, dating from 1910 onwards, to map the species’ decline and eventual extinction.
“We found that the thylacine’s distribution shrank rapidly after a period when bounties were provided for animal skins across Tasmania (1888-1909), and that the most likely location of the last surviving subpopulation was in the southwestern region,” Professor Brook said.

The team also estimated the most likely extinction date for the species, using uncertainty modelling and sensitivity analysis.
“The results showed that extinction likely occurred within four decades after the last capture, so around the 1940s to 1970s.
“But we found, through further analysis, that extinction might have been as recent as the late 1980s to early 2000s, with a very small chance that it still persists in the remote southwestern wilderness areas.”
Professor Brook said this study provided the most comprehensive and rigorous analysis of the
Thylacine’s extinction to date.
“We used a novel approach to map the geographical pattern of its decline across Tasmania, and to estimate its extinction date after taking account of the many uncertainties.
“Our findings not only shed new light on the fate of this iconic species, but also demonstrate a useful method for conservation prioritisation and search efforts for other rare species of uncertain status.”
Co-author Dr Stephen Sleightholme from the International Thylacine Specimen Database said the thylacine was one of the most fascinating and enigmatic animals of modern times.
“It has captivated the public’s imagination for decades and inspired many efforts to prove its
ongoing existence. Our study shows that there is still much to learn about its history and ecology.”





