Mysterious figure who toppled Syria’s president
After operating from the shadows for years, how did this man bring down Syria’s president and end five decades of Baath Party rule?

Abu Mohammed al-Jolani is the leader of the Islamist alliance that spearheaded an offensive that rebels say brought down President Bashar al-Assad and ended five decades of Baath Party rule in Syria.
Jolani heads Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), which is rooted in Syria’s branch of al-Qaeda.
He is an extremist who adopted a more moderate posture in order to achieve his goals.
On Sunday, as the rebels entered Damascus, he ordered all military forces in the capital not to approach public institutions.
He had earlier this week said the objective of his offensive, which saw city after city fall from government control, was to overthrow Assad.
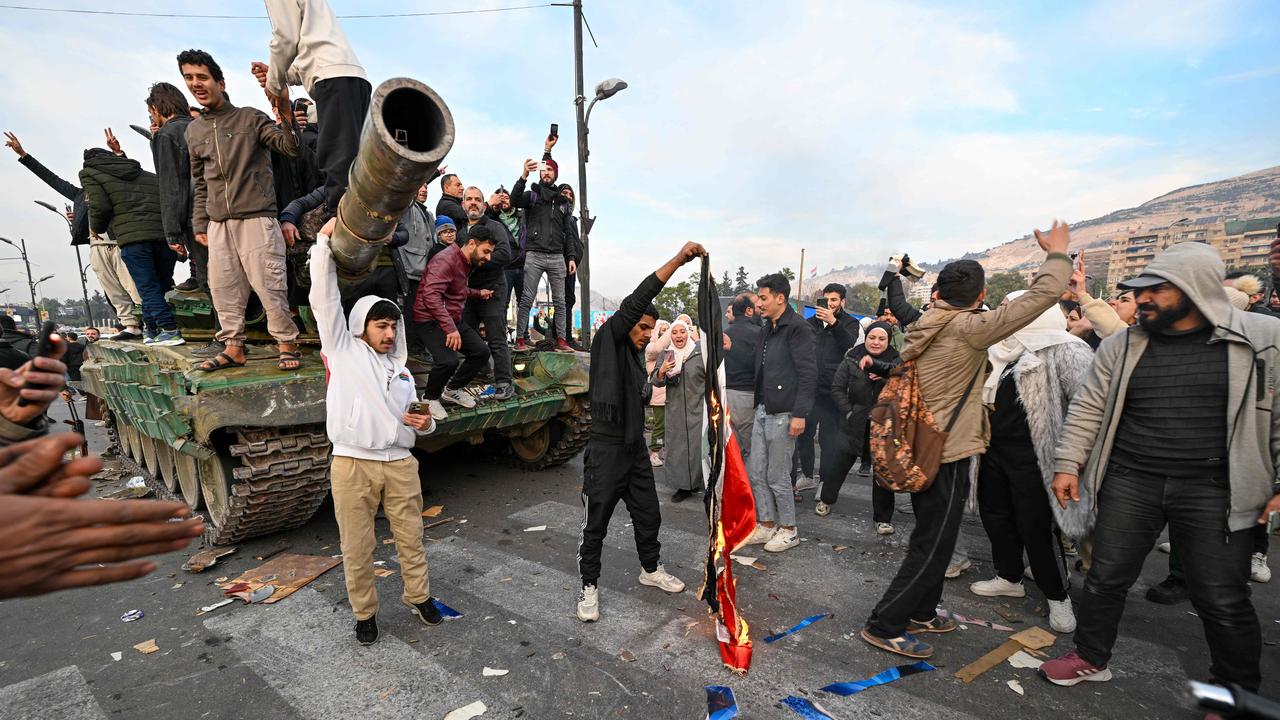
Thirteen years after Assad cracked down on a nascent democracy movement, sparking Syria’s civil war, the rebels said the president had fled the country and declared Damascus free of the “tyrant”.

Jolani had for years operated from the shadows.
Now, he is in the spotlight, giving interviews to the international media and delivering statements that have Syrians all around the world glued to their phones for clues of what the future might hold.
Earlier in the offensive, which began on November 27, he appeared in Syria’s second city Aleppo after wresting it from government control for the first time in the war.
He has over the years stopped sporting the turban worn by jihadists, often favouring military fatigues instead.
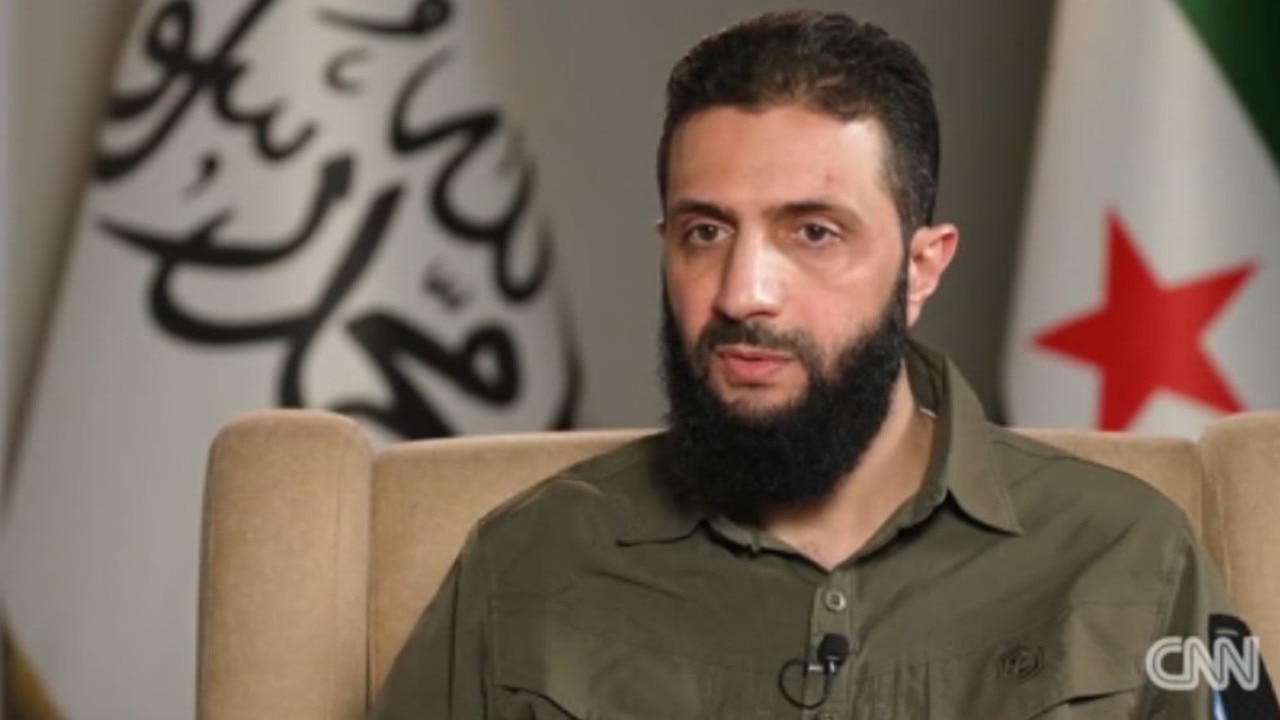

On Wednesday, he wore a khaki shirt and trousers to visit Aleppo’s citadel, standing at the door of his white vehicle as he waved and moved through the crowds.
Since breaking ties with al-Qaeda in 2016, Jolani has sought to portray himself as a more moderate leader.
But he is yet to quell suspicions among analysts and Western governments that still class HTS as a terrorist organisation.
“He is a pragmatic radical,” Thomas Pierret, a specialist in political Islam, told AFP.
“In 2014, he was at the height of his radicalism,” Pierret said, referring to the period of the war when he sought to compete with the jihadist Islamic State group.
“Since then, he has moderated his rhetoric.”


Well-to-do
Born in 1982, Jolani was raised in Mazzeh, an upscale district of Damascus. He stems from a well-to-do family and was a good student.
During the offensive, he started signing his statements under his real name – Ahmed al-Sharaa.
In 2021, he told US broadcaster PBS that his nom de guerre was a reference to his family roots in the Golan Heights, claiming that his grandfather had been forced to flee after Israel’s annexation of the area in 1967.
According to the Middle East Eye news website, it was after the September 11, 2001 attacks that Jolani was first drawn to jihadist thinking.
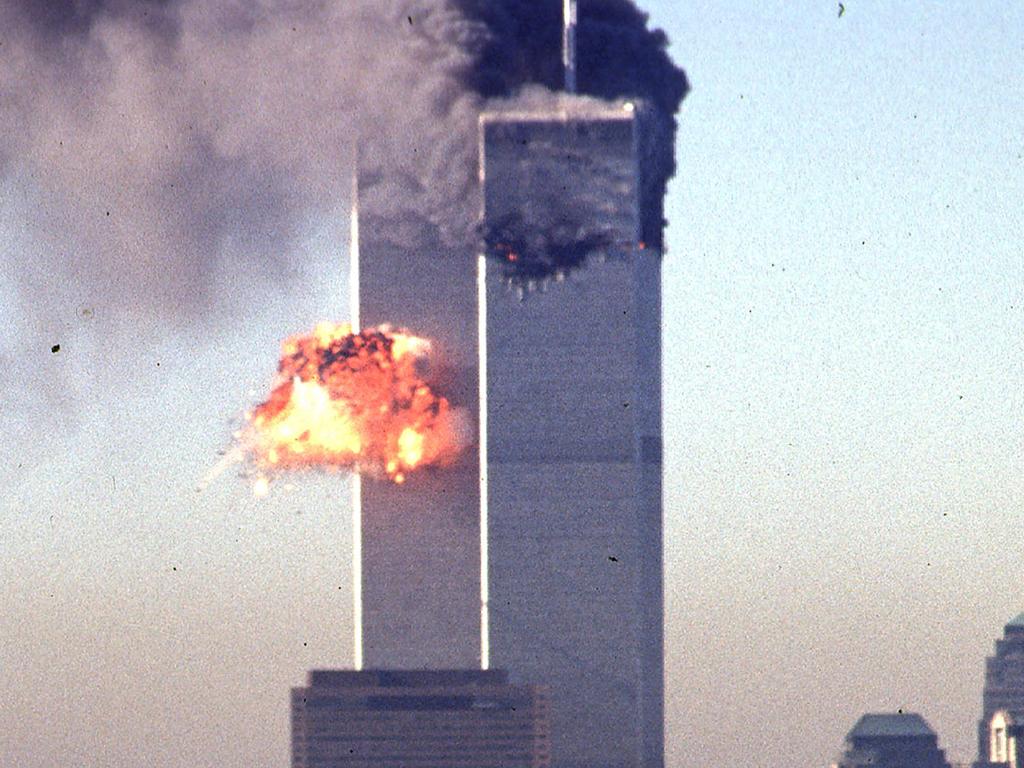

“It was as a result of this admiration for the 9/11 attackers that the first signs of jihadism began to surface in Jolani’s life, as he began attending secretive sermons and panel discussions in marginalised suburbs of Damascus,” the website said.
Following the US-led invasion of Iraq, he left Syria to take part in the fight. He joined al-Qaeda in Iraq, led by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi, and was subsequently detained for five years, preventing him from rising through the ranks of the jihadist organisation.
In March 2011, when the revolt against Assad’s rule erupted in Syria, he returned home and founded the Al-Nusra Front, Syria’s branch of al-Qaeda.
In 2013, he refused to swear allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, who would go on to become the emir of the Islamic State group, and instead pledged his loyalty to al-Qaeda’s Ayman al-Zawahiri.


‘Smart thing to do’
A realist in his partisans’ eyes, an opportunist to his adversaries, Jolani said in May 2015 that he, unlike IS, had no intention of launching attacks against the West.
He also proclaimed that should Assad be defeated, there would be no revenge attacks against the Alawite minority that the president’s clan stems from.
He cut ties with al-Qaeda, claiming to do so in order to deprive the West of reasons to attack his organisation.
According to Pierret, he has since sought to chart a path towards becoming a credible statesman.
In January 2017, Jolani imposed a merger with HTS on rival Islamist groups in northwest Syria, thereby claiming control of swathes of Idlib province that had fallen out of government hands.
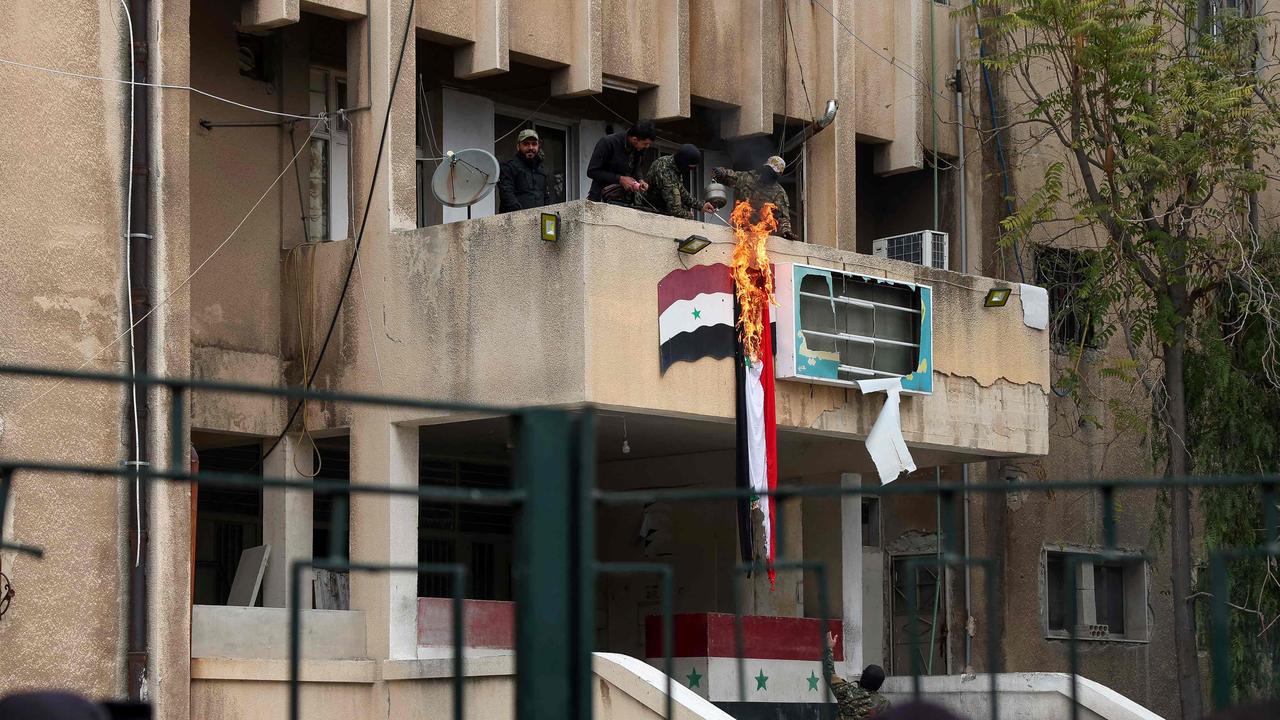

In areas under its grip, HTS developed a civilian government and established a semblance of a state in Idlib province, while crushing its rebel rivals.
Throughout this process, HTS faced accusations from residents and rights groups of brutal abuses against those who dared dissent, which the UN has classed as war crimes.
Aware perhaps of the fear and hatred his group has sparked, Jolani has addressed residents of Aleppo, home to a sizeable Christian minority, in a bid to assure them that they would face no harm under his new regime.
He also called on his fighters to preserve security in the areas they had “liberated” from Assad’s rule.
“I think it’s primarily just good politics,” said Aron Lund, a fellow at the Century International think tank.
“The less local and international panic you have and the more Jolani seems like a responsible actor instead of a toxic jihadi extremist, the easier his job will become. Is it totally sincere? Surely not,” he said.
“But it’s the smart thing to say and do right now.”